Water splitting and CO2 reduction device
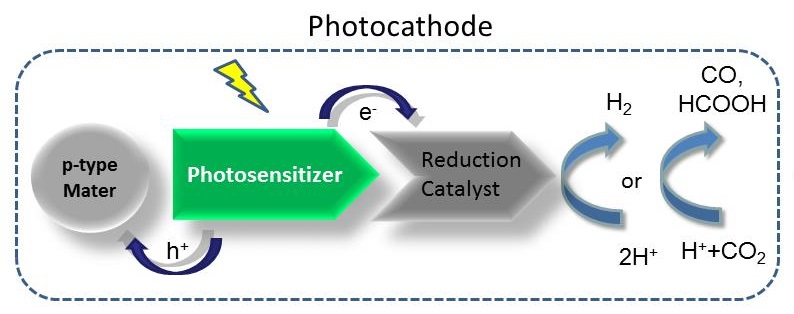
Immobilization of catalysts on photocathodes to achieve light-driven water splitting and CO2 reduction.
On the basis of study of p-type dye sensitized solar cells and organic photovoltaics, we are working on the immobilization of catalysts on different photocathodes to realize light driven water splitting and CO2 reduction. In order to make the catalyst firmly immobilized on photocathode, click chemistry is used as a effective strategy to perform this work. We transplant this concept on NiO-based electrode as well as organic photovoltaic (OPV) electrodes.
Relevant publications
- Chen Y., Chen, H., Tian H., Immobilization of a cobalt catalyst on fullerene in molecular devices for water reduction, Chem. Commun., 2015, 51, 11508-11511.
- Tian H., Molecular Catalyst Immobilized Photocathodes for Water/Proton and Carbon Dioxide Reduction, ChemSusChem 2015, 8, 3746.
- Pati. P., Zhang, L., et al., Insights into the Mechanism of a Covalently Linked Organic Dye–Cobaloxime Catalyst System for Dye-Sensitized Solar Fuel Devices, ChemSusChem, 2017, 10 (11), 2480-2495.
- Huang J., Gibert M., et al., Covalently linking CuInS2 quantum dots with a Re catalyst by click reaction for photocatalytic CO2reduction, Dalton Trans., 2018, 47, 10775-10783
